Examining Dynamic Emergent Properties of the DNA Sensing Pathway
 Feedback Mechanisms for DNA Sensing
Feedback Mechanisms for DNA SensingAbstract
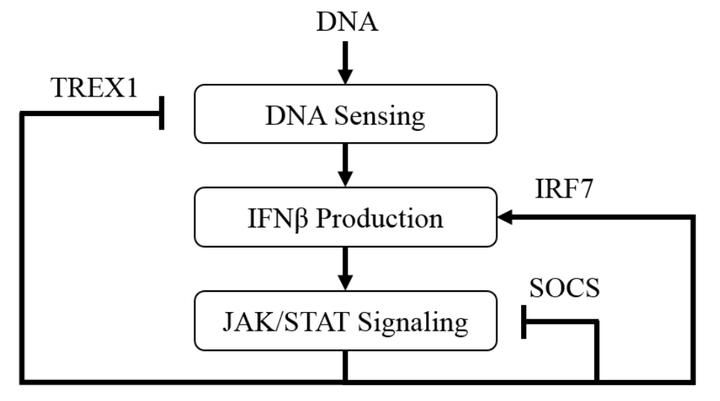
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) has recently been identified as the primary protein that detects cytosolic double stranded DNA to invoke a type I interferon response. The cGAS pathway is vital in the recognition of DNA encoded viruses as well as self-DNA leaked from the nucleus of damaged cells. Currently, the dynamics regulating the cGAS pathway are poorly understood; limiting our knowledge of how DNA-induced immune responses are regulated. Using systems biology approaches, we formulated a mathematical model to describe the dynamics of this pathway and examine the resulting system-level emergent properties. Unknown model parameters were fit to data compiled from literature using a Parallel Tempering Markov Chain Monte Carlo (PT-MCMC) approach, resulting in an ensemble of parameterized models. A local sensitivity analysis demonstrated that parameter sensitivity trends across model ensembles were independent of the select parameterization. An in-silico knock-down of TREX1 found that the interferon response is highly robust, showing that complete inhibition is necessary to induce chemical conditions consistent with chronic inflammation. Lastly, we demonstrate that the model recapitulates interferon expression data resulting from small molecule inhibition of cGAS. Overall, the importance of this model is exhibited in its capacity to identify sensitive components of the cGAS pathway, generate testable hypotheses, and confirm experimental observations.